PM (Polarization Maintaining) Faraday mirror is vital for fiber optic networks and measurement applications. It returns light with a 90° orthogonal polarization relative to the input state of polarization (SOP). In addition, it provides high stability, reliability, and low insertion loss and helps to eliminate the polarization sensitivity of an optical fiber system. This article discusses the PM Faraday mirror in detail.
What is a PM Faraday Mirror?
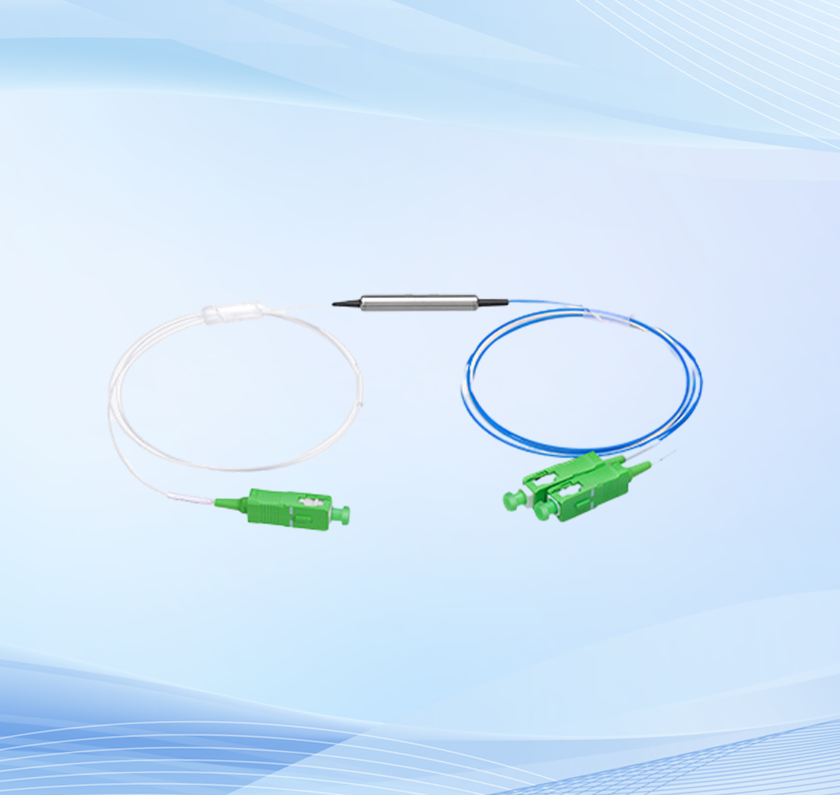
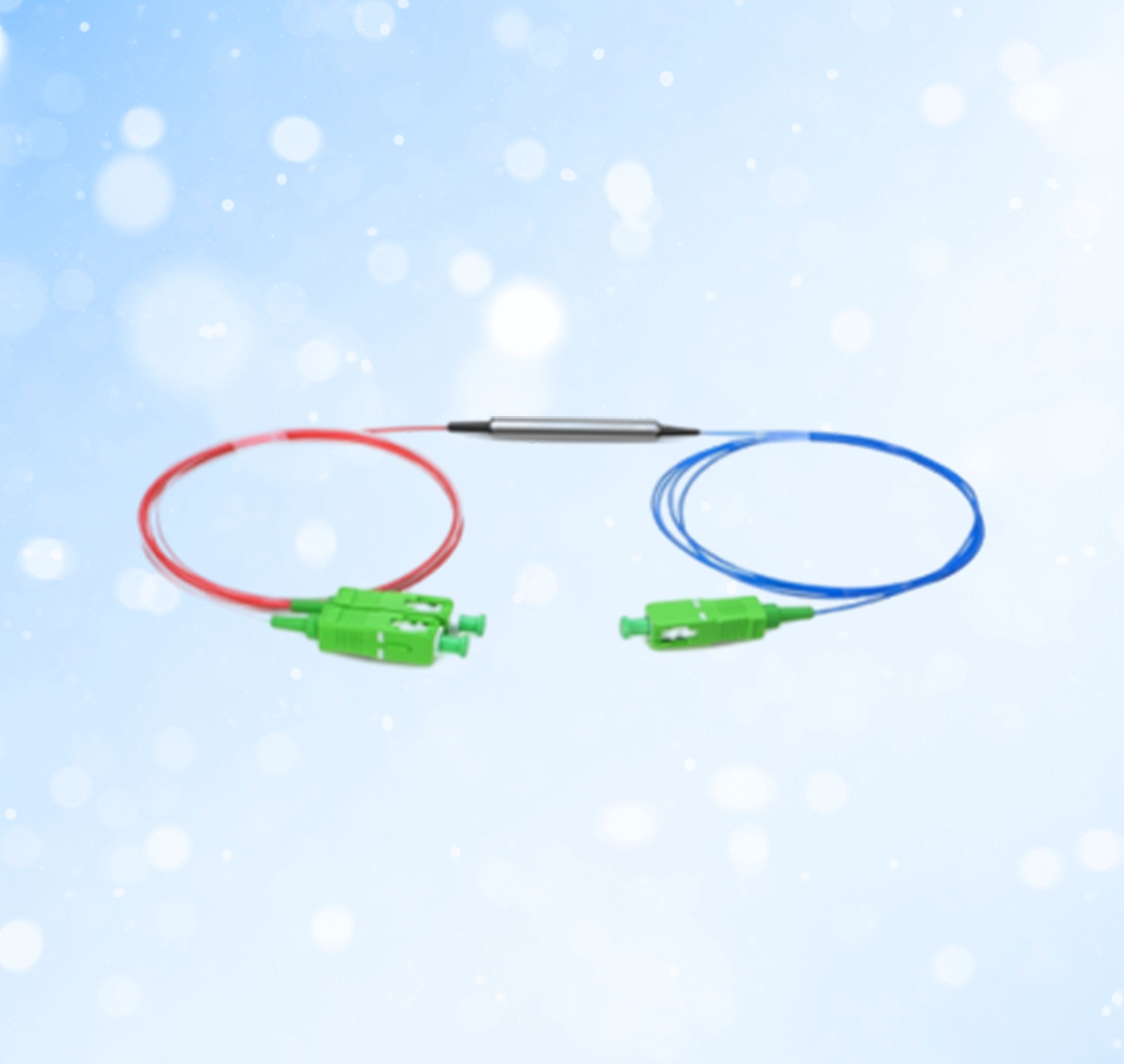
PM Faraday mirror is a passive device that provides 45 or 90-degree rotation regarding the SOP of the input light. It can help to eliminate the polarization sensitivity of an optical fiber system and polarization-induced fluctuations in fiber interferometers, Brillouin amplifiers, fiber lasers, antenna remote systems, etc. In addition, it is available in in-line and TGG (Terbium Gallium Garnet) types.

How Does a PM Faraday Mirror Work?
PM Faraday mirror works based on the Faraday Effect. In this device, a non-reciprocal rotation of an SOP occurs as the light beam passes through the optical medium within the magnetic field. It consists of a fiber collimator, a Faraday rotator, and a mirror. As the orthogonal wave light components pass the optical fiber in the forward direction, they will experience a rotation of 45 degrees in the clockwise direction. When they are reflected by the mirror, pass the Faraday rotator again. The SOP of the reflected optical signal will experience a rotation of another 45 degrees in the same direction as the input signal. Hence, the resultant rotation is 90 degrees. Now, the orthogonal components pass the fiber back but in a complimentary fiber axis and, you obtain a linearly polarized light on the close end of the fiber with a rotation of 90 degrees.
How to Achieve Rotation of the SOP in PM Faraday Mirror?
Rotation of the SOP is achieved by passing light through a Faraday rotator, which has a film of bismuth iron garnet (BIG), an external magnetic field applied to it by rare-earth magnets. A single pass through the Faraday rotator causes the SOP of light to rotate by 45° ± 1°. A planar mirror placed after the Faraday rotator returns light at the same angle of incidence; light passes through the Faraday rotator a second time, and light re-entering the input fiber has an SOP rotated 90°, or orthogonal, to the input SOP.
Features and Benefits
PM Faraday mirror provides the following features and benefits:
1. Low insertion loss and back reflection
2. Low polarization sensitivity and cost
3. High isolation and reflectivity
4. High extinction ratio and return loss
5. High reliability and stability
6. Epoxy–free optical path and compact size
7. PM Panda fiber, 250 bare fiber, 900um, 2.0mm, 3.0 loose tube
8. Connectors available FC/PC, FC/APC, FC/UPC, SC/UPC, SC/APC, LC/UPC, LC/APC
9. Center wavelengths available 1064/1310/1480/1550/1950/2000/2050nm
Applications
PM Faraday mirror is used in fiber laser, fiber optic sensing, fiber optic communication, telecommunications, coherent detecting, fiber optic amplifiers, fiber optic instruments, interferometers, fiber optic modules, antenna remote systems, LAN, CATV, EDFA, DWDM, etc.

Conclusion
PM Faraday mirror is used to minimize the polarization effect. It offers excellent performance, including low insertion loss, high-temperature stability, and epoxy–a free optical path.
Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if you have any needs.


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products



 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products




 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China