

To get the best experience for our site, we recommend you upgrade to the latest version of Internet Explorer, or select another web browser, a list of the most popular web browsers can be found below
You can download the main browser here:
 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Date: 2025-10-24 17:20:50


 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products
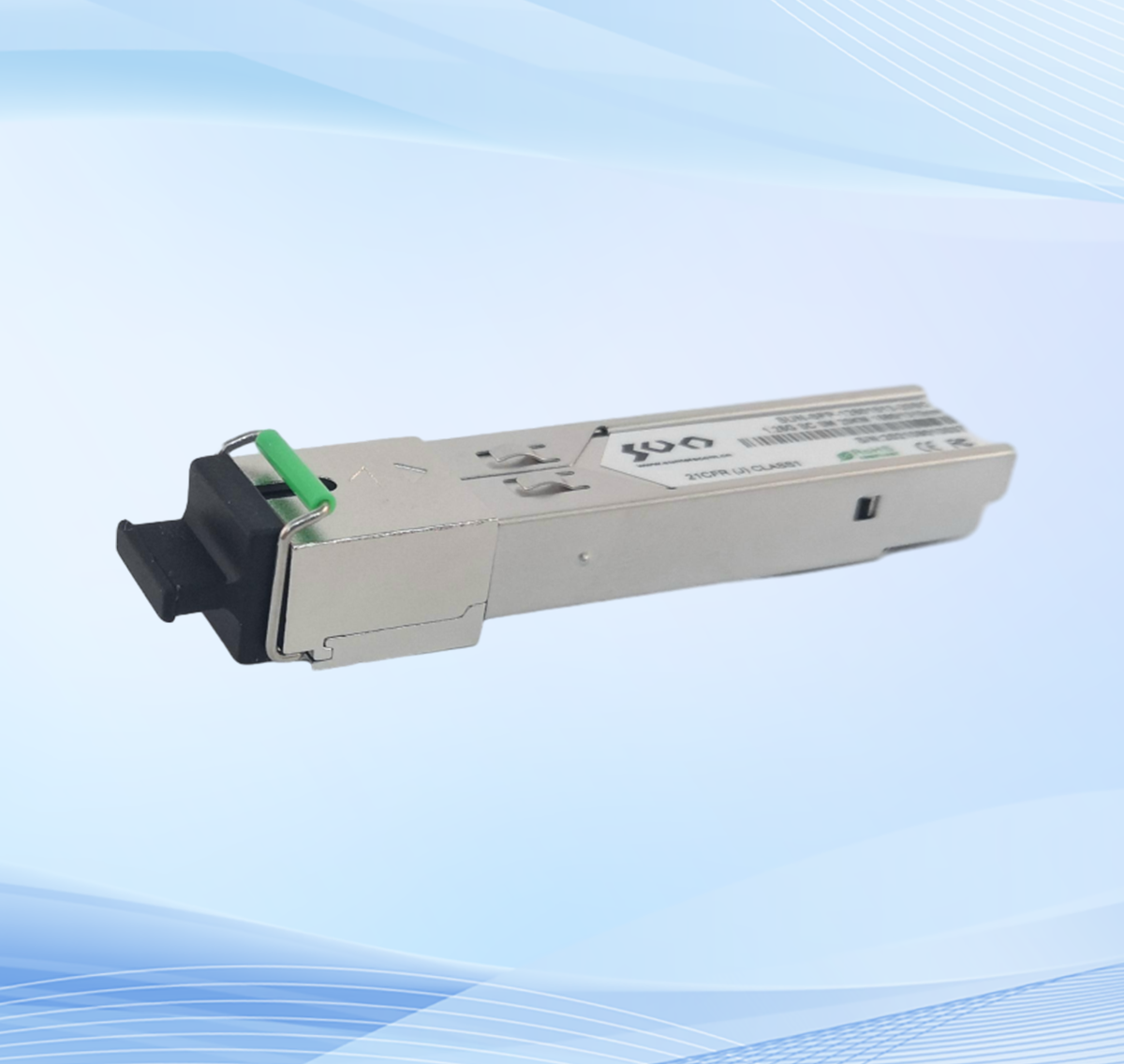

DWDM transceiver is a crucial part of the DWDM network syste...
Learn More
In the WDM Mux/Demux system, OADM (Optical Add-Drop Multiplexe...
Learn More
A dispersion compensation module (DCM) is a cost-effective sol...
Learn More
To solve some of the 400G WDM transmission problems, such as...
Learn More
Optical performance monitoring (OPM) provides cost-effective and...
Learn More ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554
 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Copyright ©1989-2025 ALL Rights Reserved
ICP (Shanghai) Number: 13005159