What is Fiber Optic Network?
A fiber optic network is the technology used to transmit information as pulses of light along a glass or plastic fiber over long distances. It offers high speed, high bandwidth, high reliability, high security, low latency, long distances, and good electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). There are several different types of fiber optic networks, such as fiber to the home (FTTH) or fiber to the premises (FTTP), fiber to the cabinet (FTTC), and fiber to the tower (FTTT). FTTH covers the entire distance from the telecom operator’s central office to the user's home. FTTC covers the section from the central office to the street cabinets, while the final connection from the cabinet to the homes uses copper cables, and FTTT connects the primary telecommunications network to the cellular network towers.

How does a fiber optic network work?
A fiber optic network is made up of cables comprising bundles of glass or plastic strands called fiber optic cables, which carry data that has been transformed into light. The light is transmitted along the fiber optic network by a laser, after having been converted by a computer into digital data signals. Light travels along the cable without leaking out by bouncing off the mirror-like walls of the glass or plastic. Fiber optic cable is composed of two layers of glass such as core and cladding. core provides the pathway for light to travel. The cladding is a layer of a glass surrounding the core .fiber optic cables can be single-mode (SM) and multi-mode (MM) fibers. SM has a smaller core and carries laser diode transmissions over long distances. MM transmits LED light through a bigger core, where light bounces in multiple paths over short distances.
Industrial Applications
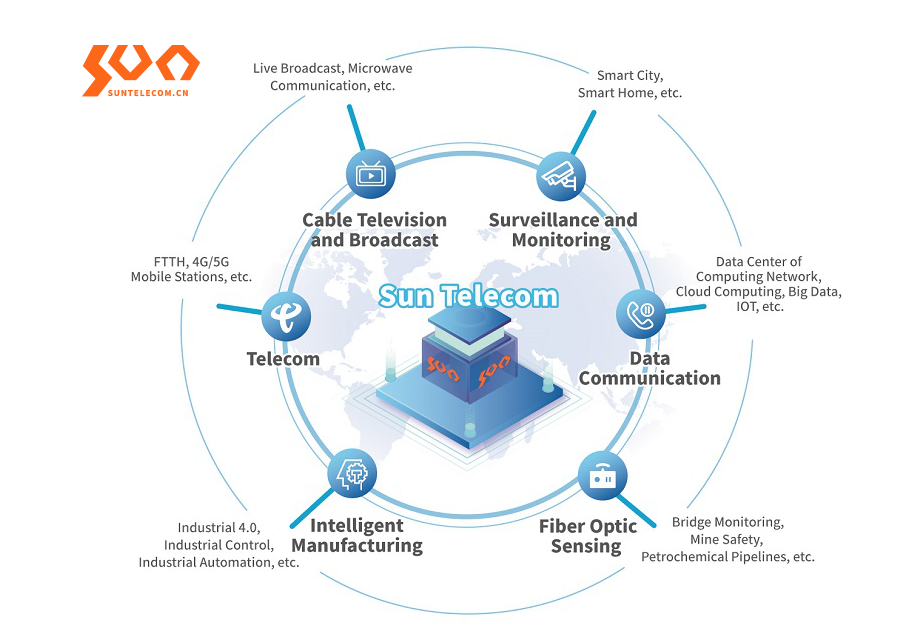
Fiber optic network in industrial applications offers enhanced performance over copper cable allowing for long distance, high speeds, high reliability, high bandwidth, higher working temperatures, immunity from electromagnetic interference, low attenuation, and much thinner and lighter. Fiber optic networks in industrial applications cover a wide variety of applications, which will be explained below.
Telecommunications Industry
Communications would not be as accessible today without the help of fiber optic networks. Their implementation has enabled people to get connected faster from long and short distances. Fiber optic networks maintain a strong signal that ensures clear communication throughout the entirety of a connection. fiber optic networks are used by the telecommunications industry to transmit telephone signals, internet, CATV, HDTV, video-on-demand, and other applications.
Computing Network Industry
It has become much easier to transfer data between computers across a network by using a high-speed fiber optic network. This allows for instant time savings and improved efficiency in the workplace, which no longer has to wait for crucial data to be transferred. For instance, modern stock exchanges depend heavily on fiber optic cable within their computer networks because they need their data transferred within the faster and shorter times possible.

Smart City Industry
As urban areas grow in complexity, the demand for intelligent systems increases. To help public administration and improve people’s lives quality, smarter solutions are needed. In the smart city, fiber optic networks expand FTTH, which is used to interconnect services such as schools, hospitals, traffic light systems (transportation), public security systems (civil defense, firefighters, police), and more. Fiber optic networks help the smart cities industry to provide communications and network infrastructure to transfer huge volumes of data to cloud-based systems.

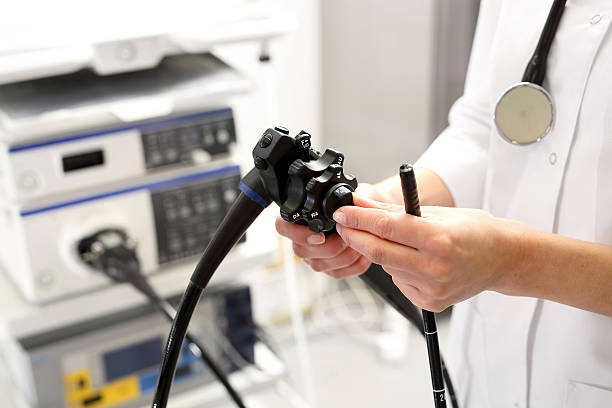
Medical Industry
Fiber optic networks are used in a variety of medical tools (endoscopes, gastroscopes, arthroscopes, and bronchoscopes) to provide precise illumination and help healthcare workers to peer closer at the causes of patients’ ailments. It also helps biomedical sensors that aid in minimally invasive medical procedures. Because the fiber optic network is not subject to electromagnetic interference, it is ideal for various tests like MRI and CAT scans, X-rays, light therapy, surgical microscopy,and removal of artery plaque, kidney stones, etc.
Military Industry
The military industry uses fiber optic networks as a means of communication and signal transfer, in addition to their ability to provide temperature sensing. It is used in aircraft and submarines to help improve the response time between command inputs and the reaction of the vehicle.
Automation Industry
Fiber optic networks are used in the automation industry to provide highly reliable networking appliances that won't fail, therefore maintaining revenue production and worker safety. It also provides an effective solution for common industry issues such as electrical noise, temperature fluctuation, high vibration, chemical exposure, and cable flexing.
Transportation Industry
Fiber optic networks are used in the transportation industry to supervise and control systems communications for railways, subways, highways, waterways, automotive, and aerospace. It also improves their safety by traffic monitoring equipment, providing real-time data control and increased bandwidth.
Energy and Utility Industry
Fiber optic networks are playing a large role in the energy and utility industry to expand alternative energy sources like renewable (wind, solar), fossil (oil, gas), nuclear, power transmission (HVDC utilities, onshore and offshore high-voltage facilities), and power distribution (sub-stations, switch-gear, smart grids). Also, help with hot spot detection and localization and ampacity (real-time thermal rating).
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, fiber optic networks provide more bandwidth in a smaller footprint, saving space, weight, and installation time. Also, help to monitor fatigue, reservoir, leaks and flow lines blockage, and thermal oil recovery.
Mining Industry
Reliable communication in harsh mining environments is important to worker safety. Fiber optic networks help to increase reliability and safety in harsh mining environments. It also offers high-speed data, low latency interference-proof, water protection, flexibility, process control, and conveyor belt monitoring in real-time to the mining industry.
Conclusion
Fiber optic networks in industrial applications cover a wide variety of applications from telecommunications to computing network ,smart city, medical, military, automation, transportation, energy and utility, oil and gas, and mining applications. However, Sun Telecom provides rugged, durable, and reliable fiber optic network products for industrial applications.


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products












 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products







 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China